You will learn to:

- use
readrand/orreadxlto import your data into R - use the interactive RStudio interface to visualise your data
- appreciate tibbles
- adjust the type of the data you would like to import
2 May 2017

readr and/or readxl to import your data into R.csv, .tsv, …).xls, .xlsx).sas from SAS, .sav from SPSS, .dta from Stata)
read.csv(), read.delim())

Use as_tibble() to convert a data.frame to a tibble
tibble vs data.framedata.frameiris
Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species 1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa 2 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa 3 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa 4 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa 5 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa 6 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 setosa 7 4.6 3.4 1.4 0.3 setosa 8 5.0 3.4 1.5 0.2 setosa 9 4.4 2.9 1.4 0.2 setosa 10 4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1 setosa 11 5.4 3.7 1.5 0.2 setosa 12 4.8 3.4 1.6 0.2 setosa 13 4.8 3.0 1.4 0.1 setosa 14 4.3 3.0 1.1 0.1 setosa 15 5.8 4.0 1.2 0.2 setosa 16 5.7 4.4 1.5 0.4 setosa 17 5.4 3.9 1.3 0.4 setosa 18 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.3 setosa 19 5.7 3.8 1.7 0.3 setosa 20 5.1 3.8 1.5 0.3 setosa 21 5.4 3.4 1.7 0.2 setosa 22 5.1 3.7 1.5 0.4 setosa 23 4.6 3.6 1.0 0.2 setosa 24 5.1 3.3 1.7 0.5 setosa 25 4.8 3.4 1.9 0.2 setosa 26 5.0 3.0 1.6 0.2 setosa 27 5.0 3.4 1.6 0.4 setosa 28 5.2 3.5 1.5 0.2 setosa 29 5.2 3.4 1.4 0.2 setosa 30 4.7 3.2 1.6 0.2 setosa 31 4.8 3.1 1.6 0.2 setosa 32 5.4 3.4 1.5 0.4 setosa 33 5.2 4.1 1.5 0.1 setosa 34 5.5 4.2 1.4 0.2 setosa 35 4.9 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa 36 5.0 3.2 1.2 0.2 setosa 37 5.5 3.5 1.3 0.2 setosa 38 4.9 3.6 1.4 0.1 setosa 39 4.4 3.0 1.3 0.2 setosa 40 5.1 3.4 1.5 0.2 setosa 41 5.0 3.5 1.3 0.3 setosa 42 4.5 2.3 1.3 0.3 setosa 43 4.4 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa 44 5.0 3.5 1.6 0.6 setosa 45 5.1 3.8 1.9 0.4 setosa 46 4.8 3.0 1.4 0.3 setosa 47 5.1 3.8 1.6 0.2 setosa 48 4.6 3.2 1.4 0.2 setosa 49 5.3 3.7 1.5 0.2 setosa 50 5.0 3.3 1.4 0.2 setosa 51 7.0 3.2 4.7 1.4 versicolor 52 6.4 3.2 4.5 1.5 versicolor 53 6.9 3.1 4.9 1.5 versicolor 54 5.5 2.3 4.0 1.3 versicolor 55 6.5 2.8 4.6 1.5 versicolor 56 5.7 2.8 4.5 1.3 versicolor 57 6.3 3.3 4.7 1.6 versicolor 58 4.9 2.4 3.3 1.0 versicolor 59 6.6 2.9 4.6 1.3 versicolor 60 5.2 2.7 3.9 1.4 versicolor 61 5.0 2.0 3.5 1.0 versicolor 62 5.9 3.0 4.2 1.5 versicolor 63 6.0 2.2 4.0 1.0 versicolor 64 6.1 2.9 4.7 1.4 versicolor 65 5.6 2.9 3.6 1.3 versicolor 66 6.7 3.1 4.4 1.4 versicolor 67 5.6 3.0 4.5 1.5 versicolor 68 5.8 2.7 4.1 1.0 versicolor 69 6.2 2.2 4.5 1.5 versicolor 70 5.6 2.5 3.9 1.1 versicolor 71 5.9 3.2 4.8 1.8 versicolor 72 6.1 2.8 4.0 1.3 versicolor 73 6.3 2.5 4.9 1.5 versicolor 74 6.1 2.8 4.7 1.2 versicolor 75 6.4 2.9 4.3 1.3 versicolor 76 6.6 3.0 4.4 1.4 versicolor 77 6.8 2.8 4.8 1.4 versicolor 78 6.7 3.0 5.0 1.7 versicolor 79 6.0 2.9 4.5 1.5 versicolor 80 5.7 2.6 3.5 1.0 versicolor 81 5.5 2.4 3.8 1.1 versicolor 82 5.5 2.4 3.7 1.0 versicolor 83 5.8 2.7 3.9 1.2 versicolor 84 6.0 2.7 5.1 1.6 versicolor 85 5.4 3.0 4.5 1.5 versicolor 86 6.0 3.4 4.5 1.6 versicolor 87 6.7 3.1 4.7 1.5 versicolor 88 6.3 2.3 4.4 1.3 versicolor 89 5.6 3.0 4.1 1.3 versicolor 90 5.5 2.5 4.0 1.3 versicolor 91 5.5 2.6 4.4 1.2 versicolor 92 6.1 3.0 4.6 1.4 versicolor 93 5.8 2.6 4.0 1.2 versicolor 94 5.0 2.3 3.3 1.0 versicolor 95 5.6 2.7 4.2 1.3 versicolor 96 5.7 3.0 4.2 1.2 versicolor 97 5.7 2.9 4.2 1.3 versicolor 98 6.2 2.9 4.3 1.3 versicolor 99 5.1 2.5 3.0 1.1 versicolor 100 5.7 2.8 4.1 1.3 versicolor 101 6.3 3.3 6.0 2.5 virginica 102 5.8 2.7 5.1 1.9 virginica 103 7.1 3.0 5.9 2.1 virginica 104 6.3 2.9 5.6 1.8 virginica 105 6.5 3.0 5.8 2.2 virginica 106 7.6 3.0 6.6 2.1 virginica 107 4.9 2.5 4.5 1.7 virginica 108 7.3 2.9 6.3 1.8 virginica 109 6.7 2.5 5.8 1.8 virginica 110 7.2 3.6 6.1 2.5 virginica 111 6.5 3.2 5.1 2.0 virginica 112 6.4 2.7 5.3 1.9 virginica 113 6.8 3.0 5.5 2.1 virginica 114 5.7 2.5 5.0 2.0 virginica 115 5.8 2.8 5.1 2.4 virginica 116 6.4 3.2 5.3 2.3 virginica 117 6.5 3.0 5.5 1.8 virginica 118 7.7 3.8 6.7 2.2 virginica 119 7.7 2.6 6.9 2.3 virginica 120 6.0 2.2 5.0 1.5 virginica 121 6.9 3.2 5.7 2.3 virginica 122 5.6 2.8 4.9 2.0 virginica 123 7.7 2.8 6.7 2.0 virginica 124 6.3 2.7 4.9 1.8 virginica 125 6.7 3.3 5.7 2.1 virginica 126 7.2 3.2 6.0 1.8 virginica 127 6.2 2.8 4.8 1.8 virginica 128 6.1 3.0 4.9 1.8 virginica 129 6.4 2.8 5.6 2.1 virginica 130 7.2 3.0 5.8 1.6 virginica 131 7.4 2.8 6.1 1.9 virginica 132 7.9 3.8 6.4 2.0 virginica 133 6.4 2.8 5.6 2.2 virginica 134 6.3 2.8 5.1 1.5 virginica 135 6.1 2.6 5.6 1.4 virginica 136 7.7 3.0 6.1 2.3 virginica 137 6.3 3.4 5.6 2.4 virginica 138 6.4 3.1 5.5 1.8 virginica 139 6.0 3.0 4.8 1.8 virginica 140 6.9 3.1 5.4 2.1 virginica 141 6.7 3.1 5.6 2.4 virginica 142 6.9 3.1 5.1 2.3 virginica 143 5.8 2.7 5.1 1.9 virginica 144 6.8 3.2 5.9 2.3 virginica 145 6.7 3.3 5.7 2.5 virginica 146 6.7 3.0 5.2 2.3 virginica 147 6.3 2.5 5.0 1.9 virginica 148 6.5 3.0 5.2 2.0 virginica 149 6.2 3.4 5.4 2.3 virginica 150 5.9 3.0 5.1 1.8 virginica
tibble vs data.frametibbleiris %>% as_tibble()
# A tibble: 150 x 5
Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <fctr>
1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
2 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa
3 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa
4 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa
5 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa
6 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 setosa
7 4.6 3.4 1.4 0.3 setosa
8 5.0 3.4 1.5 0.2 setosa
9 4.4 2.9 1.4 0.2 setosa
10 4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1 setosa
# ... with 140 more rowstibble adjusts to widthiris %>% as_tibble()
# A tibble: 150 x 5
Sepal.Length Sepal.Width
<dbl> <dbl>
1 5.1 3.5
2 4.9 3.0
3 4.7 3.2
4 4.6 3.1
5 5.0 3.6
6 5.4 3.9
7 4.6 3.4
8 5.0 3.4
9 4.4 2.9
10 4.9 3.1
# ... with 140 more rows, and
# 3 more variables:
# Petal.Length <dbl>,
# Petal.Width <dbl>,
# Species <fctr>tibble()base::data.frame() but
data.frame(`bad name` = 1:4,
x = rep(letters[1:2], 2)) %>%
str()
'data.frame': 4 obs. of 2 variables: $ bad.name: int 1 2 3 4 $ x : Factor w/ 2 levels "a","b": 1 2 1 2
tibble(`bad name` = 1:4,
x = rep(letters[1:2], 2)) %>%
str()
Classes 'tbl_df', 'tbl' and 'data.frame': 4 obs. of 2 variables: $ bad name: int 1 2 3 4 $ x : chr "a" "b" "a" "b"
tribble()~)tribble( ~x, ~y, ~z, "a", 2, 3.6, "b", 1, 8.5 )
# A tibble: 2 x 3
x y z
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 a 2 3.6
2 b 1 8.5
datapasta package
Seven file formats are supported by the readr package:
read_csv(): comma separated (CSV) filesread_tsv(): tab separated filesread_delim(): general delimited filesread_fwf(): fixed width filesread_table(): tabular files where colums are separated by white-space.read_log(): web log files
To import excel files (.xls and .xlsx):
read_excel()
read_xls()read_xlsx()
read_sas() for SASread_sav() for SPSSread_dta() for Statareadr or readxlImport Dataset button in the upper right panel or click on the file in the lower right panel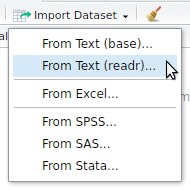
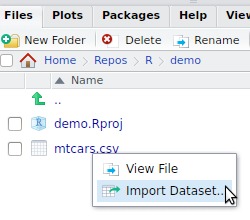
mtcars.csv file shipped with readr to your project folder:file.copy(
from = readr::readr_example("mtcars.csv"),
to = "mtcars.csv"
)Import Dataset button to import the mtcars.csv file.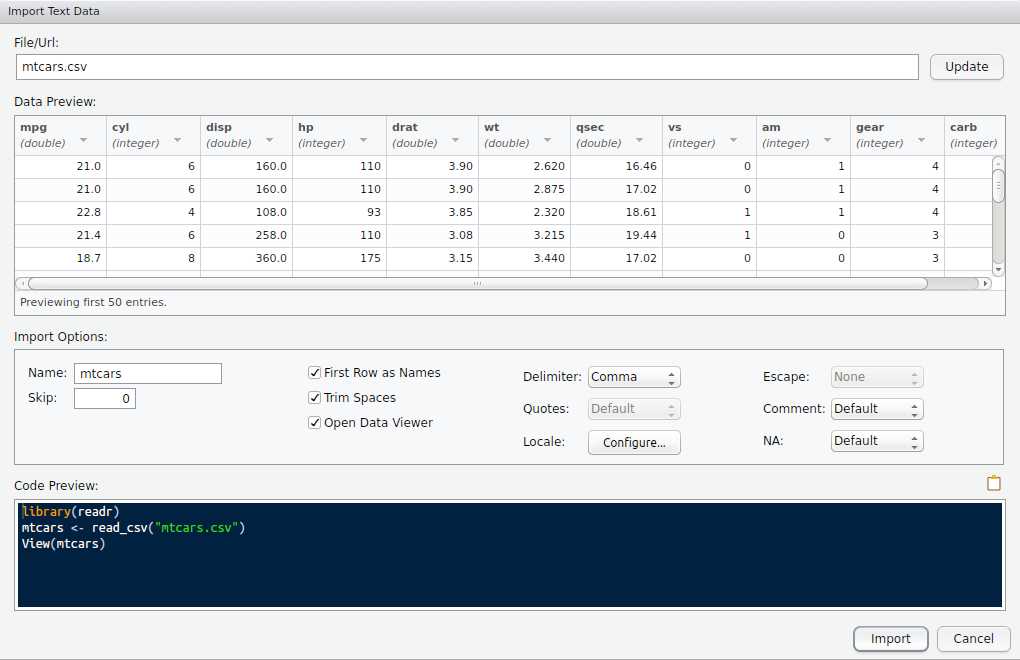
readr functionsread_csv()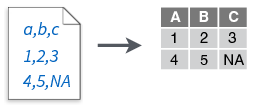
read_csv2()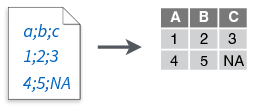
read_tsv()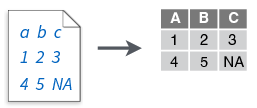
read_delim()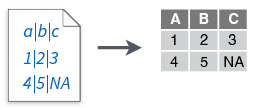
read_delim(file, delim = "|", ...)
read_fwf()
csv file: mtcars.csv"mpg","cyl","disp","hp","drat","wt","qsec","vs","am","gear","carb" 21,6,160,110,3.9,2.62,16.46,0,1,4,4 21,6,160,110,3.9,2.875,17.02,0,1,4,4 22.8,4,108,93,3.85,2.32,18.61,1,1,4,1 21.4,6,258,110,3.08,3.215,19.44,1,0,3,1 18.7,8,360,175,3.15,3.44,17.02,0,0,3,2 ...
read_csv()readr provides some example filesreadr::readr_example() to access them.zip, .gz, …)read_csv()readr_example("mtcars.csv") %>% # Generates the path to the example file
read_csv()
Parsed with column specification: cols( mpg = col_double(), cyl = col_integer(), disp = col_double(), hp = col_integer(), drat = col_double(), wt = col_double(), qsec = col_double(), vs = col_integer(), am = col_integer(), gear = col_integer(), carb = col_integer() )
# A tibble: 32 x 11
mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
<dbl> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <int> <int>
1 21.0 6 160.0 110 3.90 2.620 16.46 0 1 4 4
2 21.0 6 160.0 110 3.90 2.875 17.02 0 1 4 4
3 22.8 4 108.0 93 3.85 2.320 18.61 1 1 4 1
4 21.4 6 258.0 110 3.08 3.215 19.44 1 0 3 1
5 18.7 8 360.0 175 3.15 3.440 17.02 0 0 3 2
6 18.1 6 225.0 105 2.76 3.460 20.22 1 0 3 1
7 14.3 8 360.0 245 3.21 3.570 15.84 0 0 3 4
8 24.4 4 146.7 62 3.69 3.190 20.00 1 0 4 2
9 22.8 4 140.8 95 3.92 3.150 22.90 1 0 4 2
10 19.2 6 167.6 123 3.92 3.440 18.30 1 0 4 4
# ... with 22 more rowsguess_max optionmessage = FALSE in your rmarkdown chunk option.col_types = cols()col_types to avoid any problemParsed with column specification: cols( mpg = col_double(), cyl = col_integer(), disp = col_double(), hp = col_integer(), drat = col_double(), wt = col_double(), qsec = col_double(), vs = col_integer(), am = col_integer(), gear = col_integer(), carb = col_integer() )
Use the following functions in cols():
col_double()col_integer()col_character()col_logical()col_factor()col_date()col_datetime()col_time()col_guess()col_skip()readr_example("mtcars.csv") %>%
read_csv(col_types = cols(mpg = col_double(),
cyl = col_integer(),
disp = col_double(),
hp = col_integer(),
drat = col_double(),
wt = col_double(),
qsec = col_double(),
vs = col_integer(),
am = col_integer(),
gear = col_integer(),
carb = col_integer())
)readr_example("mtcars.csv") %>%
read_csv(col_types = cols(
mpg = "d", cyl = "i", disp = "d",
hp = "i", drat = "d", wt = "d",
qsec = "d", vs = "i", am = "i",
gear = "i", carb = "i"))
readr_example("mtcars.csv") %>%
read_csv(col_types = "dididddiiii")mtcars.csv file again but
readr_example("mtcars.csv") %>%
read_csv(col_types = cols_only(cyl = col_character(),
mpg = col_double(),
gear = col_integer()))# A tibble: 32 x 3
mpg cyl gear
<dbl> <chr> <int>
1 21.0 6 4
2 21.0 6 4
3 22.8 4 4
4 21.4 6 3
# ... with 28 more rowsreadr_example("mtcars.csv") %>%
read_csv(col_types = "dc_______i_") # A tibble: 32 x 3
mpg cyl gear
<dbl> <chr> <int>
1 21.0 6 4
2 21.0 6 4
3 22.8 4 4
4 21.4 6 3
# ... with 28 more rowschallenge.csv (provided by readr_example())challengeproblems(challenge) to list the failures againchallenge <- readr_example("challenge.csv") %>%
read_csv()Parsed with column specification: cols( x = col_integer(), y = col_character() )
Warning in rbind(names(probs), probs_f): number of columns of result is not a multiple of vector length (arg 1)
Warning: 1000 parsing failures. row # A tibble: 5 x 5 col row col expected actual file expected <int> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> actual 1 1001 x no trailing characters .23837975086644292 'challenge.csv' file 2 1002 x no trailing characters .41167997173033655 'challenge.csv' row 3 1003 x no trailing characters .7460716762579978 'challenge.csv' col 4 1004 x no trailing characters .723450553836301 'challenge.csv' expected 5 1005 x no trailing characters .614524137461558 'challenge.csv' ... ................. ... ....................................................................... ........ ....................................................................... ...... ....................................................................... .... ....................................................................... ... ....................................................................... ... ....................................................................... ........ ....................................................................... See problems(...) for more details.
challenge.csv (provided by readr_example())challengechallenge <- readr_example("challenge.csv") %>%
read_csv(col_types = "dD")challenge <- readr_example("challenge.csv") %>%
read_csv(guess_max = 1500) # n > 1000: look at the first row causing a failure
Parsed with column specification: cols( x = col_double(), y = col_date(format = "") )
skip argumentTo skip the first n rows
n_max argumentTo stop reading after n rows
col_names argumentoverride column names
readr_example("mtcars.csv") %>%
read_csv()# A tibble: 32 x 11
mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
<dbl> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <int> <int>
1 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.620 16.46 0 1 4 4
2 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.875 17.02 0 1 4 4
3 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.320 18.61 1 1 4 1
4 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.215 19.44 1 0 3 1
# ... with 28 more rowsreadr_example("mtcars.csv") %>%
read_csv(skip = 3,
n_max = 3,
col_names = FALSE)# A tibble: 3 x 11
X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 X10 X11
<dbl> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <int> <int>
1 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.320 18.61 1 1 4 1
2 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.215 19.44 1 0 3 1
3 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 3.440 17.02 0 0 3 2readr_example("mtcars.csv") %>%
read_csv(skip = 3, n_max = 3,
col_names = c("mpg", "cyl", "disp", "hp", "drat", "wt", "qsec", "vs", "am", "gear", "carb"))# A tibble: 3 x 11
mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
<dbl> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <int> <int>
1 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.320 18.61 1 1 4 1
2 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.215 19.44 1 0 3 1
3 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 3.440 17.02 0 0 3 2"name";"first_name";"born";"value" "Dupont";"Michel";03/10/71;1,2 "Doe";"John";27/02/74;1,7 "Mustermann";"Max";14/08/69;1,6
read_delim()read_delim("data/locale_1.csv",
delim = ";")
# A tibble: 3 x 4
name first_name born value
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 Dupont Michel 03/10/71 12
2 Doe John 27/02/74 17
3 Mustermann Max 14/08/69 16locale argumentread_delim("data/locale_1.csv",
delim = ";",
locale = locale(decimal_mark = ",",
date_format = "%d/%m/%y"))
# A tibble: 3 x 4
name first_name born value
<chr> <chr> <date> <dbl>
1 Dupont Michel 1971-10-03 1.2
2 Doe John 1974-02-27 1.7
3 Mustermann Max 1969-08-14 1.6?parse_datetime to list the datetime format specificationsread_csv2() is a shortcut to read_delim() using ; as a delimiter and , as the decimal markread_csv2("data/locale_1.csv",
locale = locale(date_format = "%d/%m/%y"))
read_csv2("data/locale_1.csv") %>%
mutate_at(c("born"), parse_date, format = "%d/%m/%y")readxl 
.xls and .xlsx filesread_excel()
read_xls()read_xlsx()excel_sheets() to list all sheets in the Excel filereadxl::readxl_example()
[1] "clippy.xls" "clippy.xlsx" "datasets.xls" [4] "datasets.xlsx" "deaths.xls" "deaths.xlsx" [7] "geometry.xls" "geometry.xlsx" "type-me.xls" [10] "type-me.xlsx"
readxl and the import of excel files
datasets.xlsx example filemtcars sheetfile.copy(
from = readxl::readxl_example("datasets.xlsx"),
to = "datasets.xlsx"
) # To copy it to the root of your projectdeaths datasetdeaths.xls file (using readxl_example("deaths.xlsx") to get the path to it)readxl_example("deaths.xlsx") %>%
read_excel(sheet = 1)
# A tibble: 18 x 6
`Lots of people` X__1 X__2 X__3 X__4
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
1 simply cannot resist writing <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
2 at the top <NA> of
3 or merging <NA> <NA> <NA>
4 Name Profession Age Has kids Date of birth
5 David Bowie musician 69 TRUE 17175
6 Carrie Fisher actor 60 TRUE 20749
7 Chuck Berry musician 90 TRUE 9788
8 Bill Paxton actor 61 TRUE 20226
# ... with 10 more rows, and 1 more variables: X__5 <chr>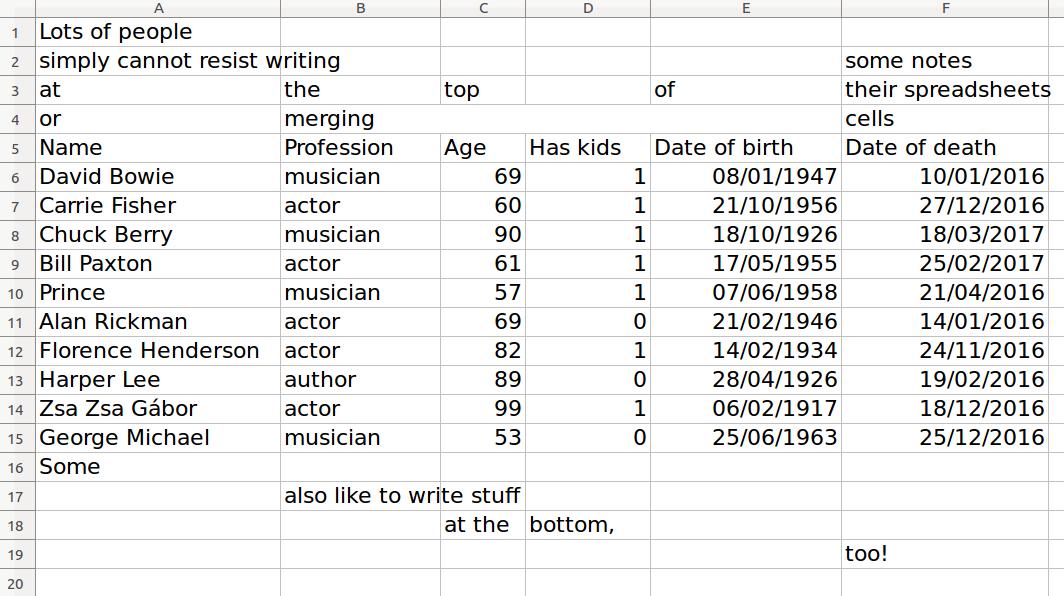

readxl 1.0.0 to read in your data frame of interest (have a look at ?readxl::read_excel)readxl_example("deaths.xlsx") %>%
read_excel(sheet = 1, range = "A5:F15")
# A tibble: 10 x 6
Name Profession Age `Has kids` `Date of birth`
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <lgl> <dttm>
1 David Bowie musician 69 TRUE 1947-01-08
2 Carrie Fisher actor 60 TRUE 1956-10-21
3 Chuck Berry musician 90 TRUE 1926-10-18
4 Bill Paxton actor 61 TRUE 1955-05-17
5 Prince musician 57 TRUE 1958-06-07
6 Alan Rickman actor 69 FALSE 1946-02-21
7 Florence Henderson actor 82 TRUE 1934-02-14
8 Harper Lee author 89 FALSE 1926-04-28
9 Zsa Zsa Gábor actor 99 TRUE 1917-02-06
10 George Michael musician 53 FALSE 1963-06-25
# ... with 1 more variables: `Date of death` <dttm>readxl_example("deaths.xlsx") %>%
read_excel(range = "arts!A5:F15")
readxl_example("deaths.xlsx") %>%
read_excel(range = cell_limits(c(5, 1), c(15, 6), "arts"))
# have a look at ?cellranger::cell_limitsreadr using the col_types argumentcols() function won't work here!
readr guesses column type based on the data.readxl guesses column type based on Excel cell typescol_types should be adjusted to a character vectorlook at the correspondance in the readxl vignette
vignette("cell-and-column-types")| How it is in Excel | How it will be in R | How to request in col_types |
|---|---|---|
| anything | non-existent | "skip" |
| empty | logical, but all NA | you cannot request this |
| boolean | logical | "logical" |
| numeric | numeric | "numeric" |
| datetime | POSIXct | "date" |
| text | character | "text" |
| anything | list | "list" |
clippy.xls example file provided by readxlreadxl_example("clippy.xls") %>%
read_excel()
# A tibble: 4 x 2
name value
<chr> <chr>
1 Name Clippy
2 Species paperclip
3 Approx date of death 39083
4 Weight in grams 0.9col_typesreadxl_example("clippy.xls") %>%
read_excel(col_types = c("text", "list"))
# A tibble: 4 x 2
name value
<chr> <list>
1 Name <chr [1]>
2 Species <chr [1]>
3 Approx date of death <dttm [1]>
4 Weight in grams <dbl [1]>readxl_example("clippy.xls") %>%
read_excel(col_types = c("text", "list")) %>%
tibble::deframe() %>%
str()
List of 4 $ Name : chr "Clippy" $ Species : chr "paperclip" $ Approx date of death: POSIXct[1:1], format: "2007-01-01" $ Weight in grams : num 0.9

readr and/or readxl to import your data into R

vignette("readr")vignette("locales")vignette("sheet-geometry")vignette("cell-and-column-types")